We offer medical and surgical options for treatment of watery eyes from blocked tear ducts.
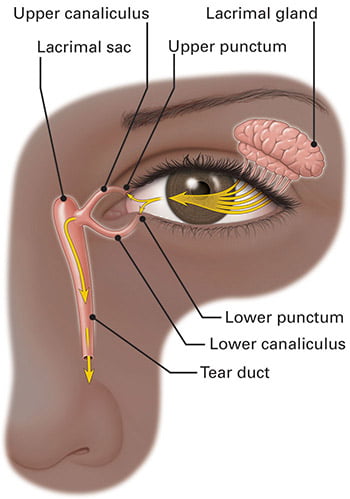
Tears are produced by the lacrimal gland that sits below the brow. Tears float along the eyelid margin to enter a tiny hole called punctum that is located in the corner near the nose.
Under the skin surface, those holes connect to delicate pipes called canaliculi. The top and bottom channels join to drain into a pipette-like structure called the tear duct.
What causes a blocked tear duct?
Tear ducts blockage can be partial or total, and can occur anywhere within the tear drainage system.
Common causes of nasolacrimal obstruction include:
- Aging
- Previous Eye Infection
- Scarring from previous surgery or injury
- Punctal narrowing from eyelid malposition
- Tear duct stones from makeup or dirt particles
- Prolonged use of medicated eye drops
- Cancer or radiation/chemotherapy treatment
- Acid Reflux
- Chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps
What are the symptoms of a blocked tear duct?
Symptoms often develop gradually and become more noticeable once a partially blocked tear duct becomes fully blocked. Commonly patients complain of:
- Constant watering, with tears flooding down the cheeks
- Blurred vision
- Rash and darkening of lower eyelid skin
- Recurrent infections, such as conjunctivitis (pink-eye)
- Eyelid crusting
Patients with total tear duct blockage often endorse worsening of their watery eye in cold weather or on windy days. Constant dabbing may result in breakdown of the lower eyelid skin.
How is a blocked tear duct diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by discovering where the blockage is located within the lacrimal system. If a blocked tear duct is suspected, your oculoplastic surgeon will conduct a tear drainage test to measure if your tears are draining properly.
After the application of topical anesthesia, a small amount of balanced salt solution will be flushed down the tear channels. If there is no blockage, water will run right down your tear duct and you will be able to feel it in the back of your nose or throat. On the other hand, if the duct is blocked, saline will reflux out through the upper channel and you will not feel any saline in your throat.
Sometimes your oculoplastic surgeon may order additional tests including imaging tests such as CT scan or MRI to rule out any sinus issues or track a special dye placed in the tear drainage system and locate any blockage.
How is a blocked tear duct treated?
Treatment of tear duct blockage follows a step-wise approach based on where the blockage is.
A narrow tear opening can be treated with a small office-based procedure called punctoplasty where the size of the punctum is widened under local anesthesia.
If the tear duct is partially blocked, your doctor may try to open the duct by flushing water through it or prescribing some medication. If this is unsuccessful or if the duct is completely blocked, tear drainage surgery called dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is typically the most effective treatment.
Depending on your specific needs, your oculoplastic surgeon may advise one of the below types of tear duct surgery:
- External DCR: A small incision is made on the top side of the nose near the bridge. The doctor removes a tiny piece of bone to recreate a new drainage channel between the lacrimal sac and the nose.
- Endonasal DCR: Tear drainage surgery performed through the nose utilizing an endoscope, a small tube with a tiny camera and light attached. The endoscopic procedure is performed similarly to external DCR without the skin incision.
- Tear duct stent Implantation: Surgical procedure in which a glass-like tube (Jones tube) is implanted behind the eyelid to facilitate tear drainage. These permanent artificial tear ducts are generally used when the nasolacrimal duct cannot be opened or repaired.
Dacryocystorhinostomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure under general anesthesia. The recovery times vary, with approximate recovery time of 1-2 weeks.

